Solutions
Osmotic Pressure
The flow of solvent can be stopped by exerting some pressure, i.e. osmosis can be stopped.
The pressure, which just stops the flow of solvent towards the solution, is called osmotic pressure.
The osmotic pressure is the excess pressure which must be applied to a solution to stop the passes of solvent towards solution, i.e. to stop the osmosis.
Since, osmotic pressure is one of the colligative properties as it depends upon the number of solute molecules instead of their properties, i.e. nature.
Experimentally, it has found that at a given temperature (T), the osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to the molarity (C).
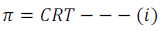
Where, π is the osmotic pressure, C is the molarity and R is the gas constant.
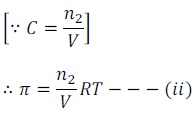
Where n2 is the number of moles of the solute and V is the volume in litre. If w2 grams of solute of molar mass M2 is present in the solution
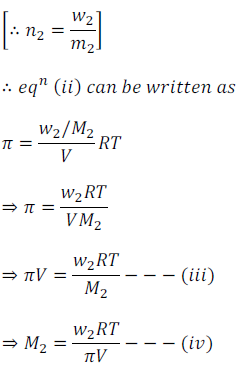
Thus, using above equation, molar mass M2 can be calculated by knowing other quantities.
This is one of the other methods, in which molar mass can be calculated by measuring osmotic pressure.
This method is used to determine molar mass of proteins, polymers and other many macromolecules.
Advantage of calculating molar mass by osmotic pressure method over other methods
In osmotic pressure method, pressure is measured around room temperature and the molarity of the solution is used instead of molality.
The determination of molar mass of solutes using osmotic pressure technique, is very useful for bio-molecules as they are generally not stable at higher temperature and polymers have poor solubility.
The magnitude of osmotic pressure is very large even for dilute solution compared to other colligative properties, this minimizes the change of error in result.
Reference: