Solutions
NCERT Exercise solution Q: 1-3
Question : 2.1 – Define the term solution. How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example.
Answer:
Soution: Solution is the homogeneous mixture of two or more components.
Example – mixture of salt and sugar, mixture of oxygen and nitrogen, mixture of sugar in water, etc.
Types of solution: In a solution, components (solute and solvent) may be solid, liquid or gas. On the basis of physical state of solvent, solutions can be divided into following three types:
- Gaseous solutions
- Liquid solutions
- Solid solutions
(a) Gaseous solution: Solutions in which solvent is gas is called gaseous solution. For example – air. Air is a mixture of many gases, such as oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide, etc.
Gasesous solution can be further classified into three types – they are
- Gas in gas (gas-gas) solution,
- Liquid in gas (liquid-gas) solution and
- Solid in gas (solid-gas) solution.
(b) Liquid solutions: Solutions in which solvent is liquid is called liquid solution. For example – solution of salt and water, solution of methanol in water.
Liquid solutions further can be divided into three types – viz.
- Solid in liquid (solid-liquid) solution,
- Liquid in liquid (liquid-liquid) solution and
- Gas in liquid (gas- liquid) solution.
(c) Solid solution: Solutions in which solvent is solid is called solid solution. For example – Alloys, hydrated salt, etc.
Solid solution can be further divided into three types – viz.
- Solid in solid (solid-solid) solution,
- Liquid in solid (liquid-solid) solution and
- Gas in solid (gas-solid) solution.
Question: 2.2 – Give an example of a solid solution in which the solute is gas.
Answer: Solution of hydrogen and palladium. In this hydrogen which is a gas is solute and palladium is solvent.
Question: 2.3 – Define the following: Mole fraction Molality Molarity Mass percentage
Answer:
(i) Mole fraction –Mole fraction is a way to express concentration of a solution.
Mole fraction of a constituent (either of solute or solvent) is the ratio of number of moles of one component to the total number of moles of all component present in a solution.
Mole fraction is denoted by letter, ‘x’.
(ii) Molality: Molality is a way to express concentration of solution.
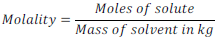
(iii) Molarity:
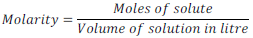
(iv) Mass percentage
Mass % of component = 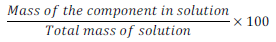
Reference: