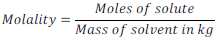Concentration of Solutions:
Amount of constituents (solute) present in a solution is called concentration. Concentration is used to describe the composition of a solution quantitatively. Concentration is described in the following ways:
(i) Mass percentage (w/w):
Mass % of component =
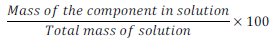
(ii) Volume percentage (%) (v/v):
Volume percentage (%) of component =
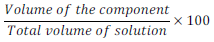
(iii) Mass by volume percentage (%) (m/v)
Mass of solute dissolved in 100ml of solution.
Mass of by volume percentage (%) to describe concentration is used generally in medicine and pharmacy.
(iv) Parts per million (ppm):
Parts per million =
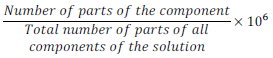
Parts per million is used to describe the concentration when solute is present in trace (very small) quantities.
(v) Mole fraction:
Mole fraction of component (x) =
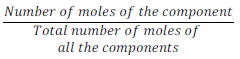
Let in a binary mixture, the number of moles of A and B are
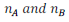 respectively
respectively
Therefore,
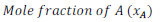
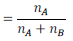
Mole fraction of a solution having i number of components
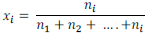
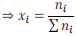
It is found that sum of all the mole fractions in a given solution is equal to unity (1).
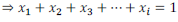
(vi) Molarity:
Number of moles of solute per liter of solution is called molarity. It is generally denoted by “ M ”.
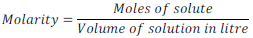
(vii) Molality:
Number of moles of solute per kg of solvent is called Molality. It is generally denoted by letter “ m ”.