Solutions
Depression of Freezing Point
Freezing point
Point at which the solid phase of a substance is in the dynamic equilibrium with the liquid phase is called freezing point.
In other words the temperature at which its liquid phase is equal to the vapour pressure in the solid phase, is called the freezing point.
The lowering of vapour pressure of a solution resulting in the lowering of freezing point compare to the the pure solvent.
According to Raoult’s Law when a non-volatile solid is added to the solvent its vapour pressure decreases and now it would become equal to that of solid solvent at lower temperature. This decreases in the freezing point of the solvent.
Let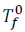 is the freezing point of pure solvent.
is the freezing point of pure solvent.
And 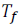 is its freezing point when non-volatile solute is dissolved in it.
is its freezing point when non-volatile solute is dissolved in it.
Therefore, the decrease in freezing point
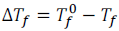 .
.
This is called the depression in freezing point.
The depression of freezing point for dilute solution (ideal solution) is directly proportional to the molality ‘m’ of the solution.
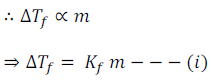
Here Kf is the proportionality constant. This depends on the nature of the solvent. This is known as the Freezing Point Depression Constant or Molal Depression Constant or Cryoscopic Constant.
Unit of 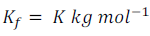
If w2 gram of the solute having molar mass equal to M2, present in w1 gram of solvent. And this produces the depression in freezing point 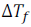 of the solvent, then molality (m) of the solute can be expressed as
of the solvent, then molality (m) of the solute can be expressed as
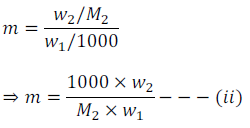
By putting the value of ‘m’ from equation (ii) in equation (i) we get
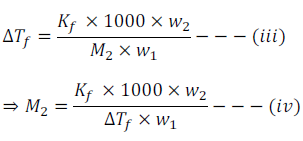
Thus by knowing other quantities molar mass of the solute can be calculated using equation (iv)
The value of 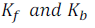 depends upon the nature of the solvent can be determined from the following equations.
depends upon the nature of the solvent can be determined from the following equations.
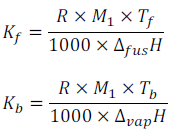
Where, R is gas constant
M1 is the molar mass of solvent.
Tf is freezing point of pure solvent in Kelvin.
Tb is the boiling point of pure solvent in Kelvin.
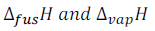 are the ethanlpies of fusion and vapourization of the solvent respectively.
are the ethanlpies of fusion and vapourization of the solvent respectively.
Reference: