Solutions
Colligative Properties
Properties of solutions which depends on the number of solute particles irrespective of their nature relative to the total number of particles present in the solution are called colligative properties.
Colligative is a Latin word (Latin ‘co’ – means together and ‘ligare’ means to bind), hence its meaning is binding together.
There are many properties which are connected with the decrease of vapour pressure of the solution and are known as collogative properties. These are
(a) Relative Lowering of vapour pressure of the solvent
(b) Depression of freezing point of solvent
(c) Elevation of boiling point of solvent
(d) Osmotic pressure of solution
Relative Lowering of Vapour Pressrue
We know that vapour pressure of a solvent in solution is less than that of the pure solvent.
According to Raoult’s Law lowering of vapour pressure of a solution depends only on the concentration of solute particles irrespective of their nature. Raoult established a relationship between vapour pressure of the solution, mole fraction and vapour pressure of the solvent. This relationship can be written as
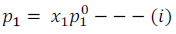
The reduction in the vapour pressure of solvent
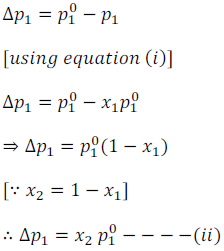
For the solution containing several non-volatile solutes, the lowering of vapour pressure depends on the sum of the mole fraction of different solutes.
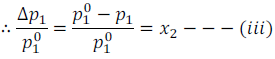
In the above equation (iii) expression 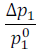 is called the relative lowering of vapour pressure and is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
is called the relative lowering of vapour pressure and is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
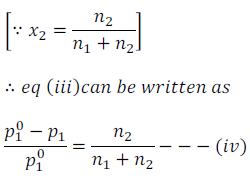
Here, n1 is the number of moles of solvent and n2 is the number of moles of the solutes present in the solution.
For dilute solution, number of moles of solute (n2) is very very less than that of number of moles of solvent (n1).
Therefore, by neglecting number of moles of solute (n2) from the denominator in the equation (iv), we get
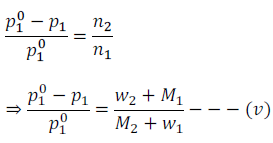
Where, w1 and w2 are the masses and M1 and m2 are the molar masses of solvent and solute respectively.
Molar mass of solute (M2) can be calculated using equation (v) after knowing all other quantities.
Reference: