Chemical Reactions and Equations - Class 10th Science
Chemical Reactions
The process in which a substance goes under chemical change and new product or producs are formed is called chemical reaction.
In other words, changes in chemical nature of substance generally denote the chemical reaction.
In a chemical reaction following changes take place:
- Change in nature of substance.
- Formation of new product.
Examples:
Burning of coal, burning of wax, respiration, digestion of food in body, etc.
Chemical reactions are generally irreversible in normal conditions. All chemical changes denote chemical reaction.
Reactants and Products
Reactant:
Initial substance or substances in a chemical reaction is called reactants. Reactants may be two or more than two.
Product:
Substance which we obtain after a chemical reaction is called product. Product may be one or more than one.
Chemical Equations:
Depiction or representation of chemical reaction in symbolic form is known as chemical equation.
Example:
(1) When magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, magnesium oxide is formed. This is a chemical reaction. This can be denoted as follows using chemical equation.
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide
Here oxygen, means burning. Whenever burning occurs, oxygen must be present there. Burning is also known as oxidation.
This is called word equation for a chemical reaction.
Here, Magnesium and oxygen are called reactants. And Magnesium oxide is called product.
(2) When zinc reacts with sulphuric acid, zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed.
Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen
Here, zinc and sulphuric acid are called reactants. And Zinc sulphate and hydrogen are called product.
Writing of a chemical equation:
While writing a chemical equation following points are taken into consideration.
- Reactants are written at the left side of the equation.
- Products are written at the right side of the equation.
- An arrow is placed between reactant and product.
- Head of arrow is generally kept towards right, i.e. towards product. In other words direction of arrow head represents the formation of product.
- Number of atoms is written in subscript using Arabic numbers after each atom if there are two or more atoms present.
- For one atom no number is written. This means if no number is written in subscript, this denotes one atom.
Writing a chemical equation using chemical symbols:
Although, a chemical equation can be written in words, but for convenience, a chemical equation is written using chemical symbols.
Example:
(1) When magnesium ribbon is burnt in air, magnesium oxide is formed. This chemical reaction can be represented as follows:
Magnesium + Oxygen → Magnesium oxide (Word chemical equation)
Mg + O2 → MgO (Chemical equation using chemical symbols)
In the above chemical equation,
Mg is symbol for magnesium.
O2 is symbol for oxygen molecule.
MgO is symbol for Magnesium oxide.
(2) When zinc reacts with sulphuric acid, zinc sulphate and hydrogen gas are formed.
Zinc + Sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen (Word chemical equation)
Zn + H2SO4 →ZnSO4 + H2 (Chemical equation using chemical symbols)
In the above chemical equation,
Zn is the symbol for Zinc,
H2SO4 is the symbol for Sulphuric acid,
ZnSO4 is the symbol for zinc sulphate and
H2 is the symbol for hydrogen gas.
Benefit of writing a chemical equation using chemical symbols:
- Takes less space.
- Can be understood clearly.
- Can be balanced easily.
Skeletal Chemical Equation
If the number of atoms of each of the elements is not equal to the number of atoms of each elements present in product, then the chemical equation is known as Skeletal Chemical Equation.
This means that if mass of elements is not equal in both sides, then the chemical equation is known as Skeletal Chemical Equation. Skeletal Chemical Equation is also known as unbalanced chemical equation.
Example:
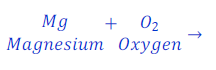
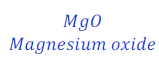
| Number of atoms in each side | ||
|---|---|---|
| Elements | No. of atoms in reactants (LHS) | No. of atoms in product (RHS) |
| Mg | 1 | 1 |
| O | 2 | 1 |
It is clear from above table that number of oxygen is not equal in both side of the given chemical equation. This means that total mass of elements in reactants is not equal to the total mass of elements present in product hence; the given chemical equation is Skeletal Chemical equation for the reaction.