Metals & Non-metals - Class 10th Science
Reaction of metals with solution of other metal salts
How do Metals react with Solutions of other Metal Salts?
When more reactive metal react with solution of less reactive metal salt, more reactive metal displace less reactive metal from its salt.
M1 + M2B(aq) → M1B(aq) + M2
Where M1 is more reactive metal than M2 and M2B is salt of metal M2.
Such reaction is known as displacement reaction or single displacement reaction.
Example:
Reaction of Iron with solution of copper sulphate
When iron nail reacts with the solution of copper sulphate, iron displaces copper and forms iron sulphate.
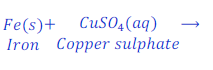
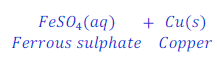
In this reaction iron is more reactive than copper.
Reaction of zinc with solution of copper sulphate
When zinc reacts with the solution of copper sulphate, zinc sulphate and copper metal is formed.
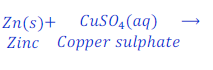
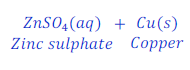
In this reaction, zinc is more reactive than copper, thus zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate.
Reaction of copper with solution of silver nitrate
When copper reacts with the solution of silver nitrate, copper displaces silver from the solution of silver nitrate and copper nitrate is formed.
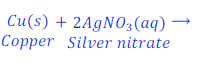
In this reaction copper is more reactive than silver
Reaction of silver with solution of copper sulphate
When silver metal is kept dipped in the solution of copper sulphate, no reaction takes place.
Silver metal + copper sulphate solution → No reaction
This happens because silver is less reactive than copper and does not displaces copper from the solution of copper sulphate.
Thus, less reactive metal do not displace more reactive metal from its salt solution.
Reactivity Series
Reactivity series is a list of metals with decreasing order of their reactivity. In this list most reactive metal is kept at the top and least reactive metal is kept in the bottom.

Most reactive metal reacts vigorously while least reactive metal do not react with normal condition. For example potassium (K) is kept in the top in the list followed by sodium (Na), calcium (Ca), Magnesium (Mg) and so on. Gold, silver, mercury and copper are kept in the bottom, these metals do not react in normal conditions and hence are called noble metals. This is one of the causes, that gold and silver metals are used in making jewelries.
Chemical properties of Non-metals
Reaction of non-metal with oxygen
Most of the non-metals form their oxides when react with oxygen.
Non metal + Oxygen → Non-metal oxide
Oxides of non metals are acidic in nature. Non-metal oxides forms acid when dissolved is water.
Example:
Reaction of carbon with oxygen
Carbon does not react with oxygen at room temperature. But, when carbon is burnt in the presence of air, it gives carbon dioxide.

Burning of carbon is an exothermic reaction. This is the cause that carbon is used as fuel. Coal, petrol, natural gas, etc. all are different forms of either carbon or carbon compounds.
Burning of carbon in insufficient supply of air
When carbon is burnt in insufficient supply of air, i.e. insufficient supply of oxygen, it gives carbon monoxide.

Reaction of sulphur with oxygen
Sulphur does not react with oxygen at room temperature. But, when sulphur is burnt in the presence of air, it gives sulphur dioxide.
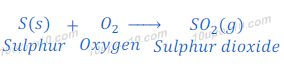
Reaction of hydrogen with oxygen
When hydrogen reacts with oxygen, it gives water.
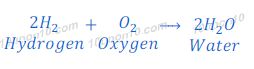
Chemical properties of non-metal oxides
Non-metal oxides are acidic in nature. Non-metal oxides turn moist blue litmus paper red. When Non-metal oxides are dissolved in water, it gives respective acid.
Example
Reaction of carbon dioxide with water
When carbon dioxide is dissolved in water, it gives carbonic acid. Carbonic acid is a weak acid.
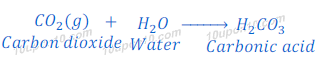
Reaction of sulphur dioxide with water
When sulphur dioxide is dissolved in water it gives sulphurous acid.
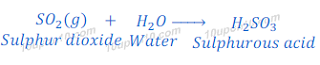
Reaction of sulphur dioxide with oxygen
When sulphur dioxide further reacts with oxygen, it forms sulphur trioxide.
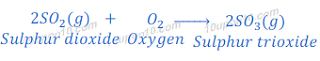
Reaction of sulphur trioxide with water
When this sulphur trioxide is dissolved in water, it forms sulphuric acid.
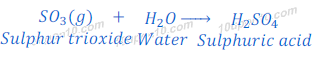
Acid Rain
Falling of acid in the form of rain is called acid rain. Factories and vehicles emit carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and many other harmful gases. These harmful gases go in air and remain present in air.
In the condition of rain carbon dioxide is dissolved in water and forms carbonic acid. On the other hand sulphur dioxide forms sulphuric acid when dissolved in water.
Carbonic acid or sulphuric acid falls on earth in the form of rain with rain water and is known as acid rain.
Acid rain is very harmful for monuments like Taj Mahal, which is made of marble. Acid rain makes water in river, pond, etc. acidic which kills the aquatic animals.