Sample Paper: Term-1:2021-22 - Class 10th Science
Science Term-1 MCQs:E
Question (41) In the given picture "A" represents
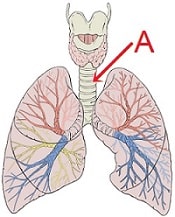
Reference: By Gray's Anatomy - Gray's Anatomy at http://www.bartleby.com/107/138.html, Public Domain, Link
(A) Rings of cartilage that ensure that the air passage does not collapse
(B) Diaphragm which contracts and flattens upon inhalation
(C) Alveoli where the exchange of gases can take place
(D) Fine hairs for air filtration
Answer (A) Rings of cartilage that ensure that the air passage does not collapse
Explanation
In the trachea many rings of cartilage are present. These rings made of cartilage ensure not to collapse while passing of air in the course of respiration.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A) Rings of cartilage which ensure that the air passage does not collapse
Question (42) Choose the incorrect option from the following:
| Option | Arteries | Veins |
|---|---|---|
| (A) Pressure | High | Low |
| (B) Wall | Thick | Thin |
| (C) Valve | Absent | Present |
| (D) Direction | Towards the heart | Away from heart |
Answer (D)
Explanation
The blood vessels called Arteries carry blood away from the heart to various organs of the body while veins collect deoxygenated blood from various parts of the body and bring it back to the heart.
The pressure of blood in arteries is high, so it has a thick wall. While the pressure of blood in veins, which collect blood from various part of the body and bring it back to the heart, has a thin wall. Veins have valves that ensure the flow of blood in only one direction.
Thus, the information given in option (D) Arteries: Towards the heart and Veins: Away from the heart, is incorrect.
Thus, the correct answer is option (D)
[Because here incorrect information is to be chosen.]
Question (43) If the incident ray coincides with the principal axis of the convex lens, then the refracted ray:
(A) Passes straight through the lens without bending
(B) Retraces back along its path
(C) Diverges on refraction through the lens
(D) Shows reflection in the same medium
Answer (A) Passes straight through the lens without bending
Question (44) If a light ray IM is incident on the surface AB making and angle of 40 degree with the surface of glass slab as shown in figure, then identify the correct emergent ray with correct angle of emergence.
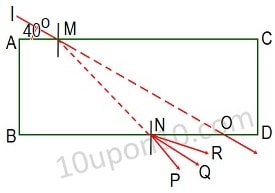
(A) Emergent ray NP and angle of emergence equal to 40 degree
(B) Emergent ray NP and angle of emergence equal to 50 degree
(C) Emergent ray NQ and angle of emergence equal to 40 degree
(D) Emergent ray NQ and angle of emergence equal to 50 degree
Answer (C) Emergent ray NQ and angle of emergence equal to 40 degree
Explanation
According to the Law of refraction of light, rays go parallel to the incident ray after emerging out the refracted ray from a glass slab to the same medium.
In the given figure NQ is parallel to IO. And, ∠ IMA = 40o.
Thus, the correct answer is option (C) Emergent ray NQ and angle of emergence equal to 40 degree
Question (45) Calculate the focal length of a spherical mirror which forms 1/3 times the magnified virtual image of an object placed 15 cm in front of it. Also, tell the nature of the spherical mirror.
(A) Convex mirror and f = 7.5 cm
(B) Convex mirror and f = – 4.5 cm
(C) Concave mirror and f = 7.5 cm
(D) Convex mirror and f = – 7.5 cm
Answer (A) Convex mirror and f = 7.5 cm
Explanation
Given, m (magnification) = 1/3
Distance of object = –15 cm
(Since object is always placed in front of the mirror, it will be always in minus)
Thus, focal length (f) = ?
In order to calculate the focal length, we need to calculate the distance of image (v) first.
Now, we know that,
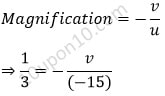
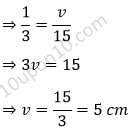
Now, we know that according to the mirror formula,
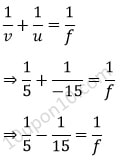
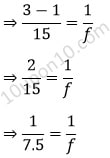
⇒ f = 7.5 cm
Here, since the value of focal length is positive, thus it is a convex mirror.
Thus, the correct answer is the option (A) Convex mirror and f = 7.5 cm
Question (46) The ray is incident at the focus of the concave lens as shown in the given figure. The refracted ray will follow which path.
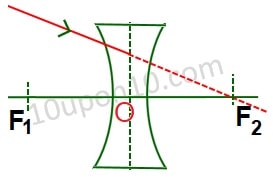
(A) The refracted ray will retrace its path back.
(B) The refracted ray passes through F2.
(C) The refracted ray gets parallel to the principal axis.
(D) The refracted ray appears to diverge from F1.
Answer (C) The refracted ray gets parallel to the principal axis.
Explanation
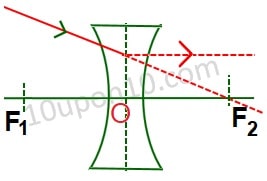
The ray incident at the focus of the concave lens passes parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
Hence, the correct answer is option (C) The refracted ray gets parallel to the principal axis.
Question (47) Magnifying glass is used to see tiny objects. What should be the distance between the magnifying glass and a tiny object to be seen through it so as to form an enlarged and erect image of an object? Also, name the lens use.
(A) Convex lens, when the object is placed at a distance less than f.
(B) Concave lens, when the object is placed at a distance less than f.
(C) Convex lens, when the object is placed between F1 and 2F1.
(D) Concave lens, when the object is placed anywhere on its principal axis.
Answer (A) Convex lens, when the object is placed at a distance less than f.
Explanation
When an object is placed between focal length (f) and pole in front of a convex lens an erected and enlarged image is formed.
Thus, the correct answer is option (A) Convex lens, when the object is placed at a distance less than f.
Question (48) A cable manufacturing unit tested a few elements on the basis of their physical properties.
Properties W X Y Z
| Malleable | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Ductile | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Electrical conductivity | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Melting point | High | Low | Low | High |
Which of the above elements were discarded for usage by the company?
(A) W, X, Y
(B) X, Y, Z
(C) W, X, Z
(D) W, X, Z
Answer (B) X, Y, Z
Explanation
The elements which are not malleable, ductile, have electrical conductivity, and have high melting points cannot be used as cable wire.
Since, elements X, Y, and Z were not malleable, ductile, and had electrical conductivity and high melting and boiling points as data given in the table, these elements were discarded by the company to use as cable wire.
Thus, the correct answer is the option (B) X, Y, Z
Section – C
This section consists of three cases followed by questions.
Case: The salt story
From: The New Indian Express 9 March 2021
The salt pans in Marakkanam, a port town about 120 km from Chennai are the third largest producer of salt in Tamil Nadu. Separation of salt from water is a laborious process and the salt obtained is used as raw materials for manufacture of various sodium compounds.
One such compound is Sodium hydrogen carbonate, used in baking, as an antacid and in soda acid fire extinguishers.
The table shows the mass of various compounds obtained when 1 litre of seawater is evaporated.
| Compund | Formula | Mass of Solid present per gm |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium Chloride | NaCl | 28.0 |
| Magnesium Chloride | MgCl2 | 8.0 |
| Magnesium sulphate | MgSO4 | 6.0 |
| Calcium Sulphate | CaSO4 | 2.0 |
| Calcium Carbonate | CaCO3 | 2.0 |
Total amount of salt obtained 45.0
Question (49) Which Compound in the table reacts with acids to relase carbon dioxide?
(A) NaCl
(B) CaSO4
(C) CaCO3
(D) MgSO4
Answer (C) CaCO3
Explanation
When calcium carbonate reacts with an acid, it gives carbon dioxide and respective salt.
Example
When calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives calcium chloride and carbon dioxide gas.
CaCO3 + HCl ⇒ CaCl2 + CO2
Thus, the correct answer is option (C) CaCO3
Question (50) How many grams of Magnesium Sulphate are present in 135 g of solid left by evaporation of sea water?
(A) 6 g
(B) 12g
(C) 18 g
(D) 24 g
Answer (C) 18 g
Explanation
As given, the mass of magnesium sulphate present in 45.0 gm of solid = 6.0 g
Thus, mass of magnesium sulphate present in 135 gm of solid = ?
∵ In 45.0 gm of solid, the mass of magnesium sulphate present = 6.0 g
∴ In 1 gm of solid, the mass of magnesium sulphate present = 6.0 g/45 g
∴ In 135 gm of solid, the mass of magnesium sulphate present = 6.0 g/45 g × 135 g = 18 g
Thus, the correct answer is option (C) 18 g