Carbon and Its Compounds - Class 10th Science
Nomenclature of Organic Compound
Need of Nomenclature
Every chemical compounds have a particular name. But carbon forms many types of structure with common molecular formula due to which names of isomers are needed to be different.
Example:
Hexane: Molecular formula: C6H14
First Structural formula of Hexane
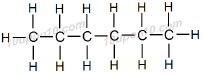
Second possible structural formula of hexane
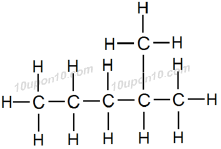
Third possible structural formula of hexane
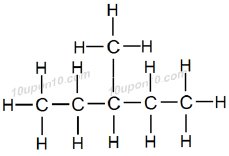
Forth possible structural formula of hexane
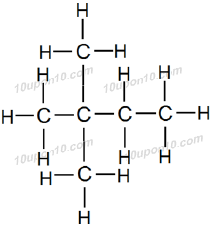
These all compounds have a general name Hexane while structural formulas of these compounds are different. Similarly many other carbon compounds exist with same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
Thus, particular naming for each of the compounds is needed to differentiate among them.
Nomenclature of Carbon Compounds
IUPAC Name: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) made some rules to name the organic compounds so that each of the organic compounds can be differentiated by their names. Such names are commonly known as IUPAC names. And process to name is called the Nomenclature of Organic Compounds.
IUPAC name are based on the name of the basic carbon chain modified by a 'prefix' or 'suffix' indicating the nature and position of the functional group.
Rules for Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
Rule no. (i): Identify the number of carbon atoms in the compound and name the compound according to the number of carbon atoms.
Example:
If number of carbon atoms = 1
∴ Name of the parent compound will be 'Methane'
If number of carbon atoms = 2
∴ Name of the parent compound will be 'Ethane'
If number of carbon atoms = 6
∴ Name of the parent compound will be 'Hexane' and so on.
Rule no. (ii) Identify the functional group if any present.
If any functional group is present, add a 'prefix' or 'suffix' specified for the functional group with the name of the parent compound.
Prefix specified for the functional group:
Halo group:
For –Cl (Chloride) functional group: Add a 'prefix' chloro with the name of parent compound.
For –Br (Bromide) functional group: Add a 'prefix' bromo with the name of parent compound.
For –I (Iodide) functional group: Add a 'prefix' Iodo with the name of parent compound.
For –F (Fluoride) functional group: Add a 'prefix' Fluoro with the name of parent compound.
Prefix is added for only Halo group. And for rest of the functional groups suffix is added.
Example:
Naming of the compound CH3Cl
Here number of carbon atom = 1
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Methane'
Now, functional group –Cl (Chloride) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add Chloro with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Chloromethane'
Structural Formula of Chloromethane
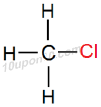
[Here functional group is indicated in red colour for convenience]
Common name for this compound: Methyl chloride
Similarly, naming for compound C2H5Cl
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 2
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Ethane'
Now, functional group –Cl (Chloride) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add Chloro with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Chloroethane' or 'Chloro–ethane'
Structural Formula of Chloroethane
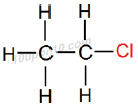
Common name for this compound: Ethyl chloride
Similarly, naming for compound C2H5Br
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 2
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Ethane'
Now, functional group –Br (Bromide) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add Bromo with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Bromoethane' or 'Bromo–ethane'
Structural Formula of Bromoethane
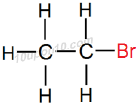
Common name for this compound: Ethyl bromide
Similarly, naming for compound C4H9F
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 4
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Butane'
Now, functional group –F (Fluoride) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add Fluoro with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Fluorobutane' or 'Fluoro–Butane'
Structural Formula of Fluorobutane
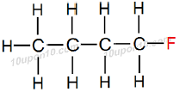
Common name for this compound: Butyl fluoride
Similarly, naming for compound C6H13I
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 6
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Hexane'
Now, functional group –I (Iodide) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add Iodo with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Iodohexane' or 'Iodo–Hexane'
Structural Formula of Iodohexane
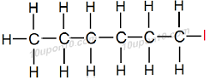
Common name for this compound: Hexyl iodide
Suffix specified for the functional group:
Naming for Alcohol (– OH) group
If alcohol (– OH) group is present in the compound, a 'Suffix' "ol" is added to the name of the parent compound.
Alkane – e + ol = Alkanol
Example:
IUPAC naming for CH3OH
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 1
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Methane'
Now, functional group –OH (Alcohol) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add "ol" as suffix with the name of the parent compound.
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Methanol'
Structural Formula of Methanol
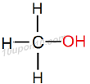
Common name for this compound is Methyl alcohol.
IUPAC naming for C3H7OH
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 3
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Propane'
Now, functional group –OH (Alcohol) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add "ol" as suffix with the name of the parent compound.
∴ Propane – e + ol = Propanol
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Propanol'
Structural Formula of Propanol
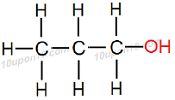
Common name for this compound is Propyl alcohol.
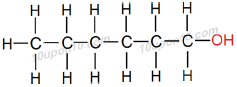
IUPAC naming for C6H13OH
Here number of carbon atom is equal to 6
Thus, name of the parent compound will be 'Hexane'
Now, functional group –OH (Alcohol) is attached with the compound.
Thus, add "ol" as suffix with the name of the parent compound.
∴ Hexane – e + ol = Hexanol
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound will be 'Hexanol'
Structural Formula of Hexanol
Naming for Aldehyde (– CHO) group
Structural formula for aldehyde group 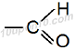
IUPAC Name of the alkane with 'aldehyde' functional group
Alkane – e + al = Alkanal
Naming of compound CH3CHO
Here number of carbon atoms in parent compound = 2
Thus, name of parent compound is 'Ethane'
Thus, functional group –CHO (Aldehyde) is attached with the compound.
Thus, a suffix 'al' is attached with the parent compound.
Thus, name of this compound
Ethane – e + al = Ethane
Hence, name of this compound will be 'Ethanal'
Structural formula of Ethanal
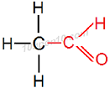
Common name of this compound: Ethanldehyde
Naming of compound C3H7CHO
Here number of carbon atoms in parent compound = 4
Thus, name of parent compound is 'Butane'
Thus, functional group –CHO (Aldehyde) is attached with the compound.
Thus, a suffix 'al' is attached with the parent compound.
Thus, name of this compound
Butane – e + al = Butanal
Hence, name of this compound will be ' Butanal'
Structural formula of Butanal
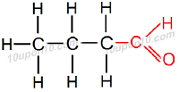
Common name for this compound: Butanaldehyde
Naming for Ketone (– CO –) group
Structural formula for ketone group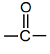
IUPAC naming: Alkane – e + one = Alkanone
IUPAC naming of CH3COCH3
Here number of carbon atoms = 3
Thus, name of parent carbon compound having three carbon atoms is Propane
Here, Ketone (– CO –) is present as functional group
∴ 'one' will be added as 'suffix' with the name of parent compound.
∴ Propane – e + one = Propanone
∴ IUPAC name of CH3COCH3 will be 'Propanone'
Structural formula of 'Propanone'
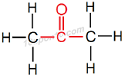
Common name of this compound: Dimethyl ketone
IUPAC naming of C2H5COCH3
Here number of carbon atoms = 4
Thus, name of parent carbon compound having three carbon atoms is Butane
Here, Ketone (– CO –) is present as functional group
∴ 'one' will be added as 'suffix' with the name of parent compound.
∴ Butane – e + one = Butanone
∴ IUPAC name of C2H5COCH3 will be 'Butanone'
Structural formula of 'Butanone'
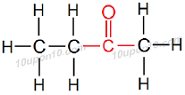
Common name of this compound is Ethyl methyl ketone.