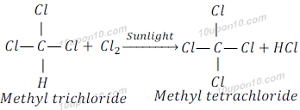Carbon and Its Compounds - Class 10th Science
Nomenclature of carbon Compound
IUPAC Naming for compounds containing Carboxylic acid (– COOH) group
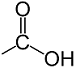
Structural formula of carboxylic acid group
IUPAC naming of alkane containing carboxylic acid group
Alkane – e + oic acid = Alkanoic acid
IUPAC naming of HCOOH
Here number of carbon atoms = 1
Thus, name of parent carbon compound having three carbon atoms is Methane
Here, Carboxylic acid (– COOH) is present as functional group
∴ 'oic acid' will be added as 'suffix' with the name of parent compound.
∴ Methane – e + oic acid = Methanoic acid
∴ IUPAC name of HCOOH will be 'Methanoic acid'
Structural formula of 'Methanoic acid'
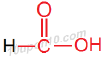
Common name of this compound: Formic acid.
IUPAC naming of CH3COOH
Here number of carbon atoms = 2
Thus, name of parent carbon compound having three carbon atoms is Ethane
Here, Carboxylic acid (– COOH) is present as functional group
∴ 'oic acid' will be added as 'suffix' with the name of parent compound.
∴ Ethane – e + oic acid = Ethanoic acid
∴ IUPAC name of CH3COOH will be 'Ethanoic acid'
Structural formula of 'Ethanoic acid'
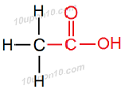
Common name of this compound: Acetic acid
IUPAC naming of C2H5COOH
Here number of carbon atoms = 3
Thus, name of parent carbon compound having three carbon atoms is Propane
Here, Carboxylic acid (– COOH) is present as functional group
∴ 'oic acid' will be added as 'suffix' with the name of parent compound.
∴ Propane – e + oic acid = Propanoic acid
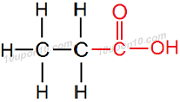
∴ IUPAC name of C2H5COOH will be 'Propanoic acid' or 'Propinoic acid'
Structural formula of 'Propanoic acid' or 'Propinoic acid'
Rule no. (iii): In the case of unsaturated hydrocarbon
Sub Rule (a): If double bond is present in the carbon chain, then 'ene' will be added in the parent name of compound after omitting 'ane'.
Sub Rule (b): If there is triple bond is present in the carbon chain, then 'yne' will be added in the parent name of compound after omitting 'ane'.
IPUAC naming of carbon compounds having double bond in carbon chain
If there is double bond present between carbon atom then a 'ene' suffix is added after omitting the 'ane'.
Example:
Alkane – ane + ene = Alkene
IUPAC Naming of C2H4
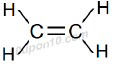
Here number of carbon atom = 2
And a double bond is present between carbon atoms.
Thus, name of parent compound: Ethane
Thus, IUPAC name: Ethane – ane + ene = Ethene
Thus, IUPAC name: Ethene
Common name of this compouond: Ethylene
IUPAC Naming of C3H6
Here number of carbon atoms present = 3
Thus, name of parent compound: Propane
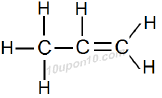
And a double bond is present between carbon atoms
Therefore, IPUAC name of the compound:
Propane – ane + ene = Propene
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound: Propene
Common name of this compound: Propylene
IUPAC Naming of C4H8
Here number of carbon atoms present = 4
Thus, name of parent compound: Butane
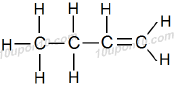
And a double bond is present between carbon atoms
Therefore, IPUAC name of the compound:
Butane – ane + ene = Butene
Thus, IUPAC name of the given compound: Butene
IPUAC naming of carbon compounds having triple bond in carbon chain
If there is double bond present between carbon atom then a 'yne' suffix is added after omitting the 'ane'.
Example:
Alkane – ane + yne = Alkyne
IUPAC Naming of C2H2
Here number of carbon atoms = 2
Thus, name of parent compound: Ethane
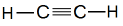
And a triple bond is present between carbon atoms.
Thus, IUPAC name of the compound
Ethane – ane + yne = Ethyne
Common name of this compound: Acetylene
IUPAC Naming of C3H4
Here number of carbon atoms = 3
Thus, name of parent compound: Propane
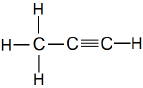
And a triple bond is present between carbon atoms.
Thus, IUPAC name of the compound
Propane – ane + yne = Propyne
IUPAC Naming of C4H6
Here number of carbon atoms = 4
Thus, name of parent compound: Butane
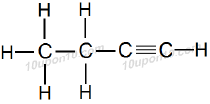
And a triple bond is present between carbon atoms.
Thus, IUPAC name of the compound
Butane – ane + yne = Butyne
Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
Combustion of carbon
All forms of carbon give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light when burn in the presence of oxygen.
When carbon is burnt in oxygen, it gives carbon dioxide, heat and light.
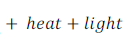
When methane (a carbon compound) is burnt in oxygen, it gives carbon dioxide, water vapour, heat and light.
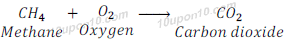
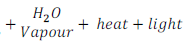
When ethyl alcohol is burnt in oxygen, it gives carbon dioxide, water vapour, heat and light.
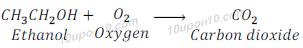
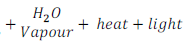
Burning of Saturated and Unsaturated Hydrocarbon
Saturated hydrocarbon burns with clean flame while unsaturated hydrocarbons burn with yellow flame and gives lots of black smoke. Because of this unsaturated hydrocarbons give sooty deposit if a metal plate or any plate is placed over the flame.
However when even saturated hydrocarbon is burnt in insufficient supply of oxygen, it also gives sooty deposit. Often it is noticed that if air hole which supply fresh air to gas burner is obstructed, flame becomes sooty and sooty deposit is noticed at the bottom of pans. This happens because of less supply of air to the flame. This is the cause that there is hole for inlet of fresh air is made in the gas/kerosene stoves so that it can give a clean blue flame.
Coal and petroleum have some amount of nitrogen and sulpur, so their combustion results in the formation of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen which creates pollution.
Oxidation
The burning of carbon in air is a type of oxidation as carbon turns into carbon dioxide.
When ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is heated with alkaline potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or acidified potassium dichromate (K2Cr2O7) it oxidized and gives Ethanoic acid [CH3COOH (Acetic acid)].
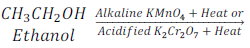
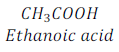
Here, alkaline potassium permanganate and acidified potassium dichromate are oxidizing agents as these supply oxygen to Ethanol.
Addition Reaction
Addition of hydrogen, chlorine, bromine, etc to unsaturated hydrocarbons is called addition reaction. Addition reaction is one of the characteristic properties of unsaturated hydrocarbons.
When Ethylene reacts with hydrogen in the present of nickel catalyst, hydrogen atoms are added to carbon atoms and gives Ethane.
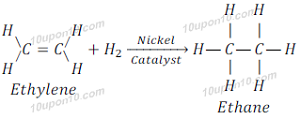
[Catalyst: Catalysts are substances that cause a reaction to proceed or occur at different rate without the reaction itself being affected.]
This addition reaction is used generally in the hydrogenation of vegetable oils using a nickel catalyst. Vegetable oils generally have long unsaturated carbon chains while animal fats have saturated carbon chains.
Saturated oils is said to be harmful for health, i.e. fats obtained from animals are harmful for health while unsaturated oils, i.e. vegetable oils are considered healthy for health. This is the cause of choosing unsaturated oils for cooking.
Substitution Reaction
Saturated hydrocarbons are generally stable and unreactive in the presence of most of the reagents. But when saturated hydrocarbon reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight, it goes under substitution reaction and chlorine replaces hydrogen.
When methane reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight, it gives methyl chloride (Chloromethane) and hydrochloric acid.
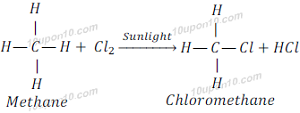
Similarly, when methyl chloride reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight, it gives methyl dichloride (Dichloromethane).
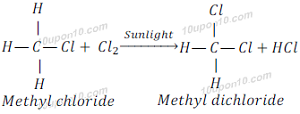
When methyl dichloride reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight, it gives methyl trichloride (Trichloromethane).
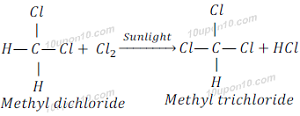
When methyl trichloride reacts with chlorine in the presence of sunlight, it gives methyl tetrachloride (Tetrachloromethane).