Carbon and Its Compounds - Class 10th Science
NCERT Exercise Solution
Question: 1. Ethane, with the molecular formula C2H6 has
(a) 6 covalent bond
(b) 7 covalent bond
(c) 8 covalent bond
(d) 9 covalent bond
Answer: (c) 7 covalent bond
Question: 2. Butanone is a four carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Answer: (c) ketone
Question: 3. While cooking, if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the outside, it means that
(a) the food is not cooked completely
(b) the fuel is not burning completely
(c) the fuel is wet
(d) the fuel is burning completely
Answer: (b) the fuel is not burning completely
Question: 4. Explain the nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Answer:
Valence electrons of carbon = 4
Valence electron of hydrogen = 1
Valence electrons of chlorine = 7
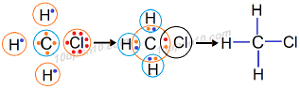
Carbon shares one valence electrons with each of the three hydrogen atoms, i.e. total three electrons with hydrogen atoms and one electron with chlorine atom. On the other hand each of the three hydrogen atoms share one electron with carbon atom and chlorine atom shares one electron with carbon atom in order to achieve their stable configuration and formation of bonds.
Since total four pair of electrons is shared among carbon, hydrogen and chlorine atoms, thus four bonds are formed in the formation of chloromethane.
Al bonds are formed because of sharing of electrons, so bonds are formed called covalent bonds. Covalent bonds so formed are highly stable.
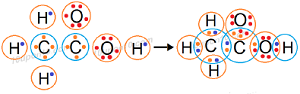
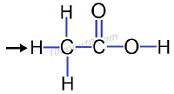
Question: 5. Draw the electron dot structures for
(a) ethanoic acid
Answer:
(b) H2S
Answer:

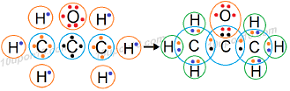
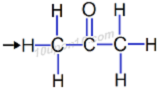
(c) propanone
Answer:
(d) F2
Answer:

Question: 6. What is an homologous series? Explain with an example.
Answer: Series of carbon compounds having same general formula regardless of functional groups are called HOMOLOGOUS SERIES. Members of compounds of a homologous series have similar chemical properties.
Example:
CH4 (Methane), C2H6(Ethane), C3H8(Propane), C4H10(Butane) and so on forms a homologus seris.
CH3OH, C2H5OH, CH5OH, and so on forms a homologous series. Members of this homologous series are alcohols.
Question:7. How can ethanol and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical properties?
Answer:
Difference in physical properties of Ethanol and Ethanoic acid
(a) Ethanol has a special type of odour while ethanoic acid is odourless liquid.
(b) Ethanol is a volatile liquid while ethanoic acid is non volatile
(c) Melting point of ethanol is – 117.150C while melting point of ethanoic acid is 16.850C.
(d) Boiling point of ethanol is 77.850C while boiling point of ethanoic acid is 117.850C.
Difference in Chemical properties of Ethanol and Ethanoic Acid
(a) Ethanol has no effect on litmus paper while ethanoic acid turns blue litmus paper red.
(b) Ethanol does not react with carbonate or hydrogen carbonate while ethanoic acid gives carbon dioxide gas when reacts with carbonate or hydrogen carbonate.
(c) Ethanol burns with clean flame while ethanoic acid does not burn.
Question:8. Why does micelle formation take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed in other solvent such as ethanol also?
Answer: Soap molecules have two ends in water solution, one is hydrophilic and other end is hydrophobic. Hydrophilic end is soluble in water and hydrophobic solution is soluble in grease. When soap is added to water, hydrophilic ends get dissolved in water while hydrophobic ends get dissolved in dirt present in water mixed with grease. Because of these properties soap molecules get arranged into a special orientation and form micelles when dissolved in water.
This is the cause that soap forms micelles when dissolved in water. Soap does not form such micelles in other solvent such as ethanol.
Question: 9. Why are carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications?
Answer: Carbon and most of the carbon compounds, such as petrol and petroleum products, have high calorific value and give lot of heat. This is the cause that carbon and its compounds used as fuels for most applications.
Question: 10. Explain the formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap.
Answer: Hard water contains salts of calcium and magnesium. Presence of these salts is the cause of hardness of water.
When soap is treated with hard water, most of the soap molecules react with salts of magnesium and calcium present in hard water and form insoluble substance and less lather. Insoluble substance formed after reaction of soap molecules with salt of calcium and magnesium present in hard water is called scum.
Question: 11. What change will you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red and blue)?
Answer: Soap molecules are basic in nature. Thus, when red litmus paper is dipped in the soap solution, it turns red because of basic nature of soap. There is no change in colour when a blue litmus paper is dipped in soap solution.
Question: 12. What is hydrogenation? What is its industrial application?
Answer: The addition of hydrogen to the unsaturated hydrocarbons to convert them into saturated one in the presence of catalyst, such as nickel, palladium, etc. is called hydrogenation. These reactions are known as addition reactions also as hydrogen are added to unsaturated hydrocarbon in this.
Industrial application:
(a) Hydrogenation is done to convert unsaturated vegetable oils to saturated one. Saturated fats are desirable over unsaturated fats because of health point of view. On the other hand saturated fats are almost non reactive and hence can be stored for long time compare to liquid fats.
(b) Liquid petrochemicals are turned into semi solid, such as paraffins (wax) and cycloalkanes (naphthenes) using hydrogenation of unsaturated petroleum products.
Question: 13. Which of the following hydrocarbons undergoes addition reactions:
C2H6, C3H8, C3H6, C2H2 and CH4.
Answer: Addition reactions are the addition of hydrogen to the unsaturated hydrocarbons to make them saturated.
In the given lists of hydrocarbons, only C3H6 (Propene), C2H2 (Ethyne) is an unsaturated hydrocarbons, thus C3H6 (Propene), and C2H2 (Ethyne) undergo addition reaction.
Question: 14. Give a test that can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Answer: Butter is a saturated compound while cooking oil is unsaturated. Unsaturated hydrocarbon decolorize the bromine water while saturated does not.
Thus, using bromine water test butter and cooking oil can be differentiated chemically.
Take two test tubes and pour some butter in one and some cooking oil in other.
Add bromine water in both of the test tubes.
Test tube in which bromine water decolorizes has cooking oil and test tube in which bromine water is not decolorized has butter.
Question: 15. Explain the mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Answer: When soap is mixed in water, it forms a structure called micelles. Because of formation of micelles we see the foam of soap in water.
In micelles one end of soap molecule is towards the oil while the ionic end faces outside. This forms an emulsion in water.
Dirt in clothes contains oil which gets stuck with clothes. When cloth is dip in soap water, soap micelle helps in dissolving dirt present in cloths and water which can be washed out while rinsing, this cleans the cloths.