Light: Reflection & Refraction - Class 10th Science
Refraction by a Spherical Lens
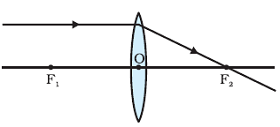
Refraction of Rays coming parallel to principal axis to convex lens
Rays coming parallel to the principal axis are passes through the principal focus after refraction from a convex lens.
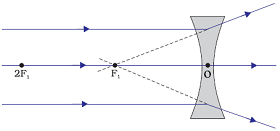
Refraction of Rays coming parallel to principal axis to concave lens
Rays coming parallel to the principal axis are appeared to passes through the principal focus after refraction from a concave lens.
Refraction of Ray of light passing through the principal focus from a convex lens
A ray of light passing through the principal focus emerges parallel to the principal axis after refraction from a convex lens.
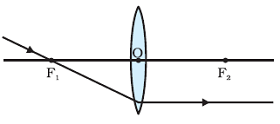
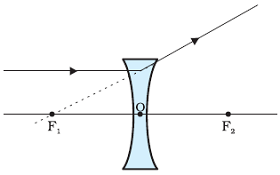
Refraction of Ray of light passing through the principal focus from a concave lens
A ray of light appearing to meet at the principal focus of a concave lens will emerge parallel to the principal axis after refraction.
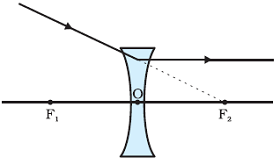
Refraction of Ray passing through the optical centre of a spherical lens
A ray of light passing through the optical centre of a lens will emerge without any deviation after refraction from a spherical lens.
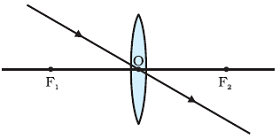
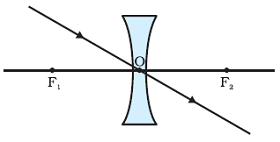
Image Formation by Convex Lens
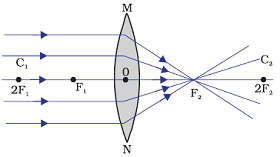
Image formation by a convex lens when object is at infinity
When object is at infinity, image is formed by a convex lens is at principal focus.
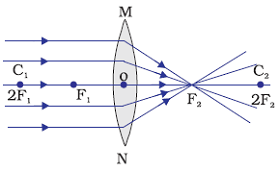
Position of image: At focus F2
Relative size of the image: Highly diminished, point sized
Nature of the image: Real and inverted
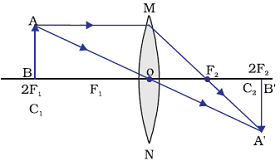
Image formation by a convex lens when object is beyond centre of curvature (C1)
When object is beyond centre of curvature (C1), i.e. beyond 2F1 of a convex lens, image is formed between principal focus (F2) and centre of curvature (C2 or 2F2).
Position of image: between principal focus (F2) and centre of curvature (C2 or 2F2)
Relative size of the image: Diminished
Nature of the image: Real and inverted
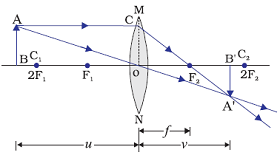
Image formation by a convex lens when object is at centre of curvature (C1 or 2F1)
When object is at 2F1, i.e. at centre of curvature (C1), image is formed at other side of centre of curvature (C2), i.e. at 2F2 by a convex lens.
Position of image: At 2F2 i.e. at centre of curvature (C2)
Relative size of the image: Same size
Nature of the image: Real and inverted
Image formation by a convex lens when object between F1 and 2F1
When object is placed between F1 and 2F1, an enlarge image is formed beyond 2F2 by a convex lens.
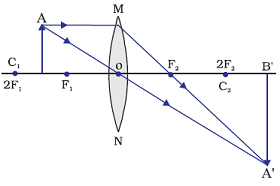
Position of image: Beyond 2F2 i.e. beyond centre of curvature (C2)
Relative size of the image: Enlarged
Nature of the image: Real and inverted
Image formation by a convex lens when object is at Focus (F1)
When image is placed at focus (F1), a highly enlarge image is formed at infinity by a convex lens.
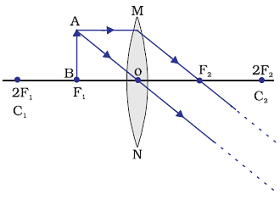
Position of image: At infinity
Relative size of the image: Highly Enlarged
Nature of the image: Real and inverted
Image formation by a convex lens when object between focus (F1) and optical centre (O)
When object is placed between focus (F1) and optical centre (O), an enlarge image is formed at same side beyond 2F1 by a convex lens.
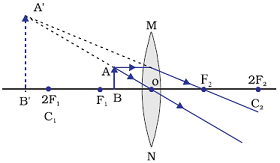
Position of image: At same side beyond 2F1
Relative size of the image: Enlarged
Nature of the image: Virtual and Erect
Image Formation by Concave Lens
Similar to a convex mirror only two conditions arise to place an object infront of a concave mirror for image formation. These positions are
First object is at infinity and second object is between infinity and optical centre (O).
Image formation by a concave lens when object is at infinity
When object is placed at infinity, a diminished imaged is formed by a concave lens at focus (F1).
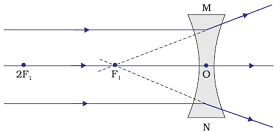
Position of image: At focus (F1)
Relative size of the image: Highly diminished, point sized
Nature of the image: Virtual and Erect
Image formation by a concave lens when object is between infinity and optical center (O)
When object is placed between infinity and optical centre (O), a diminished image is formed between focus (F1) and optical centre by a concave lens.
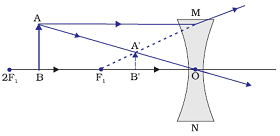
Position of image: Between focus (F1) and optical centre (O)
Relative size of the image: Diminished
Nature of the image: Virtual and Erect