Light: Reflection & Refraction - Class 10th Science
NCERT Exercise Solution
Question: 1. Which one of the following materials cannot be used to make a lens?
(a) Water
(b) Glass
(c) Plastic
(d) Clay
Answer: (d) Clay
Explanation: Clay is an opaque material while water, glass and plastic are transparent. Thus, clay cannot be used to make a lens.
Question: 2. The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be virtual, erect and larger than the object. Where should be the position of the object?
(a) Between the principal focus and the centre of the curvature
(b) At the centre of curvature
(c) Beyond the centre of curvature
(d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus
Answer: (d) Between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus
Explanation: A virtual and erect image is formed only when object is placed only between the pole of the mirror and its principal focus.
Apart from this by placing object at all other possible positions, a real image is formed by a concave mirror.
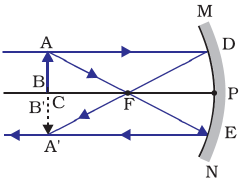
Question: 3. Where should an object be placed in front of a convex lens to get a real image of the size of the object?
(a) At the principal focus of the lens
(b) At twice the focal length
(c) At infinity
(d) Between the optical centre of the lens and its principal focus
Answer: (b) At twice the focal length
Explanation: When object is placed at 2F1, i.e. at twice of the focal length, an inverted, equal sized and real image is formed at 2F1 by a convex lens.
Question: 4. A spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have each a focal length of –15 cm. The mirror and the lens are likely to be
(a) Both concave
(b) Both convex
(c) the mirror is concave and the lens is convex
(d) the mirror is convex, but the lens is concave
Answer: (a) Both concave
Explanation: Distance of a concave mirror and concave lens is measured with negative sign according to sign convention.
Here, since, focal length is given with negative sign, thus, given lens and mirror is concave.
Question: 5. No matter how far you stand from a mirror, your image appears erect. The mirror is likely to be
(a) Plane
(b) Concave
(c) Convex
(d) either plane or convex
Answer: (d) either plane or convex
Explanation: A plane mirror and a convex mirror always forms and erect image intead of the distance of object from the mirror.
Thus, option (d) either plane or convex is the correct answer.
Question: 6. Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50cm.
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50cm.
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5cm
Answer: (c) A convex lens of focal length 5cm
Explanation: When object is placed between F1 and optical centre, a real, enlarged and erected image is formed beyond 2F2 by a convex lens.
Thus, it is convenient to use a convex lens of focal length of 5cm while reading small letters found in a dictionary. Convex lens with this focal length will produce image at a convenient distance to read.
If a convex lens having focal length of 50cm is used, then image formed by it will be at a distance of more than 1meter, to read at such distance will not be convenient.
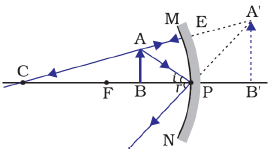
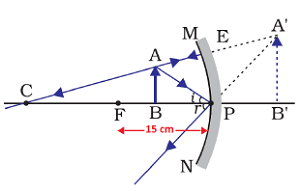
Question: 7. We wish to obtain an erect image of an object, using a concave mirror of focal length 15cm. What should be the range of distance of the object from the mirror? What is the nature of the image? Is the image larger or smaller than the object? Draw a ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
Answer: A concave mirror forms a virtual, enlarged and erect image only when object is placed between its principal focus and pole.
Thus, in given situation of a concave lens having focal length equal to 15cm, the object must be placed less than 15cm from pole of the mirror to get an erect image.
Thus, range of distance of the object from the mirror = less than 15cm
Nature of image: Virtual and erect
Size of image: Larger than the object
Question: 8. Name the type of mirror used in the following situations.
(a) Headlights of a car
(b) Side/rear view mirror of a vehicle
(c) Solar furnace
Support your answer with reason.
Answer:
(a) Headlights of a car: Concave mirror is used.
Explanation: When object is placed at principal focus of a concave mirror, rays coming from object direct parallel to the principal axis and a highly enlarged, real and inverted image is formed at infinity.
Thus, in headlights of a car, by placing bulb (source of light) at principal focus of a concave mirror, a parallel beam of light is obtained which goes up to infinity. This facilitates better vision upto a long distance to the driver.
(b) Side/rear view mirror of a vehicle: A convex mirror is used.
Explanation: A concave mirror is used as side/rear view mirror of a vehicle because:
A convex mirror gives an erect and smaller image.
A convex mirror has wider field of view as it is curved outwards which enable a driver to view much larger area than would be possible with a plane mirror.
A convex mirror enables the driver to see traffic behind him because of features given above and facilitate safe driving.
(c) Solar furnace: A concave mirror is used having large aperture.
Explanation: A concave mirror converges light rays coming parallel to its principal axis from infinity at its principal focus.
By converging rays of light at a point, all heat of light get focused at one point and produce enormous heat.
Thus, in a solar furnace, a concave mirror having large size of aperture is used.