Light: Reflection & Refraction - Class 10th Science
In Text Solution
Question: 1. Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
Answer: Rays coming from infinity are parallel to the principal axis pass through a point of spherical mirror. This point is called FOCUS or PRINCIPAL FOCUS of a spherical mirror. Focus is known as Focal Point also.
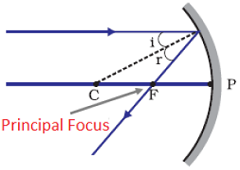
Focus of a concave mirror lies in front of reflecting surface while in the case of convex mirror Focus lies behind the reflecting surface.
Focus or Principal Focus is denoted by letter 'F'.
Question: 2. The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. What is its focal length.
Answer: Radius of curvature = 2 x Focal length
Here given, Radius of curvature = 20 cm
Therefore, Focal length = 20 cm / 2
Or, Focal length = 10 cm Answer
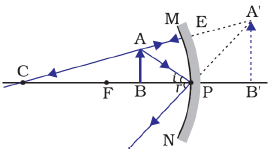
Question: 3. Name the mirror that can give and erect and enlarged image of an object.
Answer: Concave mirror
Explanation: A concave mirror produces an erect and enlarged image behind the mirror when object is placed between F (Focus) and P (Pole).
Question: 4. Why we prefer a convex mirror as a rear view mirror in vehicles?
Answer: A concave mirror is preferred as a rear view mirror in vehicles because
A convex mirror gives an erect and smaller image.
A convex mirror has wider field of view as it is curved outwards which enable a driver to view much larger area than would be possible with a plane mirror.
A convex mirror enables the driver to see traffic behind him because of features given above and facilitate safe driving.
Question: 5. Find the focal length of a convex mirror whose radius of curvature is 32 cm.
Answer: Given, Radius of curvature = 32 cm
We know that Focal length = Radius of curvature / 2
Therefore, Focal length = 32 cm / 2 = 16 cm Answer
Question: 6. A concave mirror produces three times magnified (enlarged) real image of an object placed at 10 cm in from of it. Where is the image located?
Answer: Given,
Distance of object (u) = – 10 cm (Since, object is infront of mirror, thus a minus sign is added before the distance of object)
Magnification (m) = 3
Distance of image (v) = ?
We know that
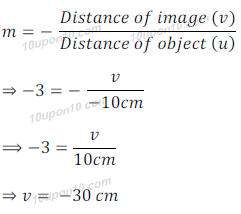
Here, minus sign before the distance of image shows that image is formed infront of mirror and image is real.
Thus location of image is 30 cm in front of concave mirror.
Question: 7. A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards the normal or away from the normal? Why?
Answer: When ray of light travelling in air enter obliquely into water, it bends towards the normal.
When ray of light enters from optically rarer medium to denser medium, it bends towards normal and vice versa. This is called refraction of light. This happens because light travels at higher speed in optically rarer medium and its speed decreases when enters in a optically denser medium.
Here, water is optically denser medium than that of water. Since, speed of light is greater in air than water, thus when light enters in water from air, it bends towards normal.
Question: 8. Light enters from air to glass having refractive index 1.50. What is the speed of light in the glass? The speed of light in vacuum is 3 x 10 8 m s –1.
Answer: Given,
Speed of light in vacuum (c) = 3 x 10 8 m s –1
Since, speed of light in air is almost similar to that of vacuum,
Thus, speed of light in air = 3 x 10 8 m s –1
Refractive Index of glass (ng = 1.50
Speed of light in the given glass (v) = ?
We known that,

Question: 9. Find out, from Table 10.3, the medium having highest optical density. Also find the medium with lowest optical density.
Answer: As given in table 10.3
Refractive Index of air = 1.0003
And Refractive Index of diamond = 2.42
Refractive Index is reciprocal of optical density. This means refractive index increases with decrease in optical density and vice versa. Medium which has lower optical density is rarer medium and that having higher optical density is denser medium.
Since, diamond has highest Refractive Index and air has lowest Refractive Index
Thus, Diamond has lowest optical density and air has highest optical density.
Question: 10. You are given kerosene, turpentine and water. In which of these does the light travel fastest? Use the information given Table 10.3.
Answer: According to Table 10.3
Refractive Index of Kerosene = 1.44
Refractive Index of turpentine = 1.47
Refractive Index of water = 1.33
Medium which has higher Refractive Index is optically denser medium. And light travels with lower speed in optically denser medium and vice versa.
Here Refractive Index of the water is lowest, i.e. 1.33 compare to kerosene and turpentine.
Thus, light travels with fastest speed in water among given medium, i.e. kerosene, turpentine and water.
Question: 11. The refractive index of diamond is 2.42. What is the meaning of this statement?
Answer: Refractive Index of a medium tells that how much denser or rarer a medium is. Medium having higher Refractive Index is optically denser medium.
Here, given the refractive index of diamond is 2.42, this statement tells that diamond is optically highly denser medium.
Question: 12. Define 1 dioptre of power of a lens.
Answer: If focal length is expressed in meters, then power is expressed in diopters.
Thus, 1 diopter of power of a lens whose focal length is 1 meter
Or, 1D = 1m –1
Question: 13. A convex lens forms a real and inverted image of a needle at a distance of 50cm from it. Where is the needle placed in front of the convex lens. If the image is equal to the size of the object? Also, find the power of the lens.
Answer: When object is placed at the 2F1 of a convex lens, an equal size image is formed at the other side, i.e. at 2F2 of the convex lens.
Here, given
Distance of image = 50cm
Therefore, distance of object = – 50cm
Thus, needle is placed at 2F1 in front of the convex lens.
We know that, focal length of a convex lens = 2F1 /2
Here, Radius of curvature = 2F1 = 50cm = 0.5m
Or, Focal length (f) = 0.50 m / 2 = 0.25m
We know that power of a lens (P) = 1/f
Or, P = 1/0.25m
Or, P = + 4 dioptre
Hence, needle is placed at 2F1 in front of the convex lens, i.e. 50cm in front of convex lens.
And power of lens = + 4 dioptre
Question: 14. Find the power of a concave lens of focal length 2m.
Answer: Given, focal length (f) = 2m
We know that power of a lens (P) = 1/f
Or, P = 1/2m = 0.5 dioptre
Since, lens is concave, thus power will be in minus.
Thus, power of given lens = – 0.5 dioptre